Laravel Many-to-many eloquent relationships are a little bit more complicated than hasOne and hasMany relationships. An example of many to many relationships is a user with may have multiple roles, where the role are also connected with multiple users. We can define many to many relationships by using belongToMany() helper with a pivot table.
So in this tutorial, you are going to learn how to create many-to-many relationships with migration with a foreign key schema for one to many relationships, use sync with a pivot table, create records, attach records, get all records, delete, update, where condition and everything related to many to many relationship.
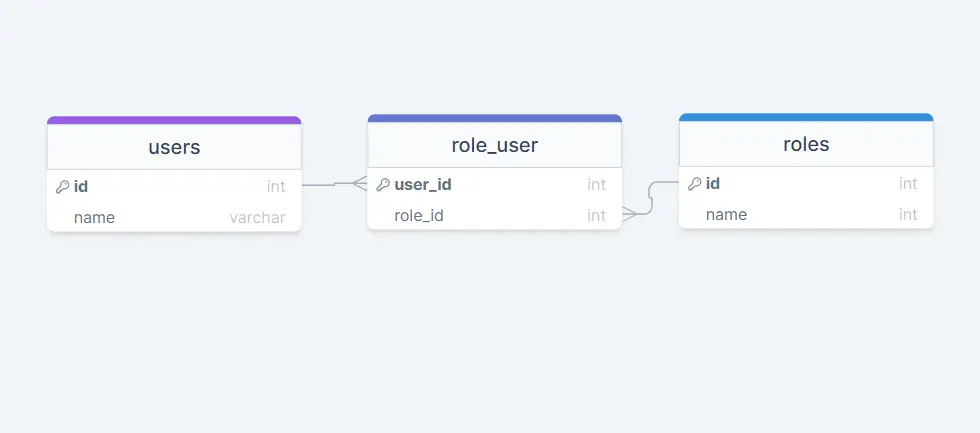
Table Structure Of Many to Many
To define belongsToMany() relationship, three database tables are needed: users, roles, and role_user. The role_user table is called pivot table and derived from the alphabetical order of the related model names and contains user_id and role_id columns. This table will be used as an intermediate table linking the users and roles.
users
id - integer
name - string
roles
id - integer
name - string
role_user
user_id - integer
role_id - integer
Defining Many to Many Relationship
Many-to-many relationships can be defined by writing a method that returns the result of the belongsToMany method. So we can create a many to many relationship with roles for a user like:
app/Models/User.php
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class User extends Model
{
/**
* The roles that belong to the user.
*/
public function roles()
{
return $this->belongsToMany(Role::class, 'role_user');
}
}
Now define the same relationship in the Role model:
app/Models/Role.php
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Role extends Model
{
/**
* The users that belong to the role.
*/
public function users()
{
return $this->belongsToMany(User::class, 'role_user');
}
}
Read also: Laravel One To One/HasOne Eloquent Relationship Tutorial
Once the relationship is defined, you may access the user's roles using the roles dynamic relationship property:
App\Http\Controllers\TestController.php
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\Models\User;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
class TestController extends Controller
{
public function index($id)
{
$user = User::find($id);
foreach ($user->roles as $role) {
//
}
}
}
Create Records with Many to Many Relationship
If you want to save data with many to many relationships using eloquent, then we can use sync or attach method like:
App\Http\Controllers\TestController.php
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\Models\Post;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
class TestController extends Controller
{
public function index($id)
{
$user = User::find($id);
$roleIds = [1, 2];
$user->roles()->attach($roleIds);
}
}
Or you can use sync also like:
App\Http\Controllers\TestController.php
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\Models\Post;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
class TestController extends Controller
{
public function index($id)
{
$user = User::find($id);
$roleIds = [1, 2];
$user->roles()->sync($roleIds);
}
}
Read also: Complete Explanation With Example On Laravel Middleware
Conclusion
Now we know laravel 9 many to may relationships and how it works. Hope this Laravel 9 belongsToMany relationship tutorials will help you. Now we know how to use sync or attach with many to many relationships.
